Background
During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Kazakhstan (June 2020), the media reported multiple cases of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-negative pneumonia with increased mortality. Our objective was to study the epidemiological characteristics of hospitalized patients with positive and negative PCR with analysis of hospital and post-hospital mortality. We also compare the characteristics of respiratory diseases between 2019 and 2020.
Methods
The study population consists of 17,691 (March-July-2020) and 4,600 (March-July-2019) hospitalized patients with respiratory diseases (including COVID-19). Incidence rate, case fatality rate, and survival analysis for overall mortality (in-hospital and post-hospital) were evaluated.
- Study population and data sources
The study population consisted of all hospitalized patients with respiratory illnesses (including COVID-19) according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) from March to July 2019 and from March to July 2020 in Turkestan oblast, Kazakhstan. The following ICD-10 codes were included in the study: J00-J06 (acute upper respiratory tract infections), J09-J18 (influenza and pneumonia), J20-J22 (other acute lower respiratory tract infections), J40- J47 (chronic diseases of the lower respiratory tract), J96-J99 (other diseases of the respiratory system), B34 (viral infection of unspecified site), Z20 (contact and “suspected” exposure to communicable diseases), U07.1 (COVID-19 specified virus) and U07 .2 (COVID-19 unspecified virus).
The raw data was retrieved from the Single National Electronic Health System (UNEHS) linked with the records to the “Electronic Registry of Internal Patients” that included data on dates of admission and discharge, ICD-10 codes, dates and results of PCR tests, discharge results and some demographic data. Global mortality statistics (in-hospital and post-hospital death) were obtained independently from the “Adjunct Population Registry” and were linked to hospitalized patients through the Population Registry Number (RPN-ID); each date of death followed by the date of hospital discharge is considered post-hospital mortality. The population census of the Turkestan oblast, including all cities and rural areas (2,016,100 people), was obtained from the State Statistics Committee.
- SARS-CoV-2 infection detection method
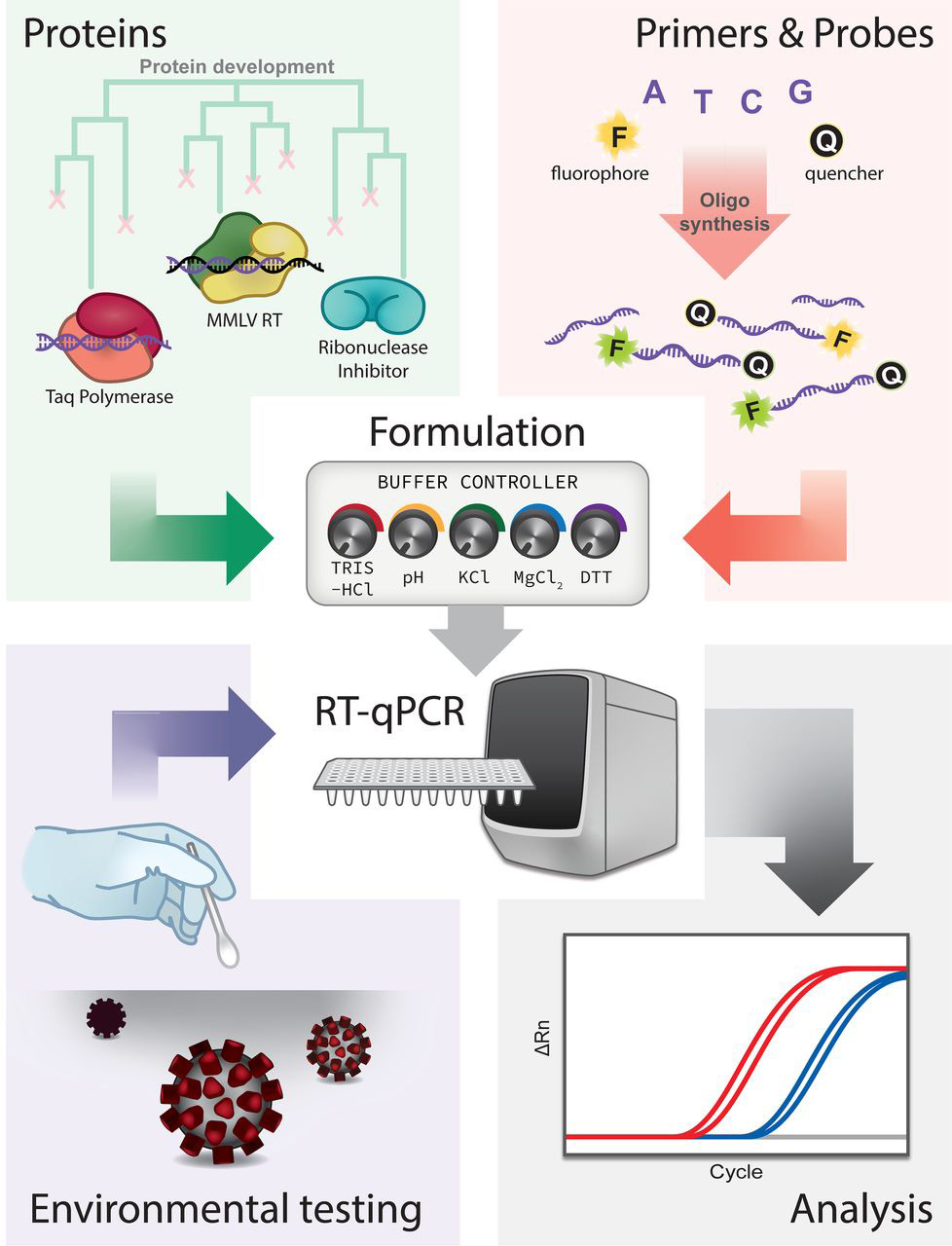
Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection was performed by real-time quantitative PCR on nasopharyngeal swabs with the BGI kit (Beijing Genomics Institute, Shenzhen, China) in defined special regional laboratory settings.
- Assessment results
Incidence, mortality and lethality rates were evaluated. Incidence and mortality rates were calculated for each year using the number of newly diagnosed patients and deaths, and the size of the population. The case fatality rate was calculated by dividing the number of deaths by the number of newly diagnosed cases. The incidence was compared by year of admission. All-cause mortality was divided into in-hospital and post-hospital mortality, which was used to identify associated risk factors among admissions in 2020.
The start of follow-up was the date of hospital admission, and patients were followed until death or the end of the follow-up period (August 30, 2020). Two outcome variables were of interest for survival analysis: in-hospital mortality (time from hospital admission to hospital discharge) and overall (in-hospital and post-hospital combined) mortality (time from hospital admission to death at any time up to 30 days). August 2020). ). Censoring for in-hospital mortality survival analysis was taken on the date of hospital discharge, and for pooled mortality, it was August 30, 2020.
- Statistic analysis
For each diagnostic group, absolute numbers of hospitalizations and deaths, incidence and mortality rates per 100,000, case fatality rates per year were reported. Absolute and relative frequencies were reported for categorical variables. Means and standard deviations were used to describe continuous variables, while biased continuous variables were characterized by medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs). Parametric bivariate analysis (Pearson’s Chi-squared, two-sample t-test, ANOVA) was used to assess associations of demographic and disease-related characteristics with outcome variables.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves were plotted for the results of the PCR test. Cox proportional hazards models were fitted with epidemiologically and statistically significant covariates using backwards stepwise selection. The proportional hazards assumption for different groups was tested using log plots. We performed a sensitivity analysis to assess the robustness of our main findings.
We examined the association between overall mortality (in-hospital and post-hospital) and sociodemographic parameters in a subgroup of patients admitted to only provisional and infectious disease hospitals (excluding patients who were in quarantine). The significance level of 5% (α < 0.05) was taken. All statistical analyzes were performed using STATA 16.0 statistical software. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Ethics Committee (NU-IREC 203/29112019) with exemption from informed consent.
Results
Respiratory disease incidence and mortality rates were 4 and 11 times higher in 2020 compared to 2019 (877.5 vs. 228.2 and 11.2 vs. 1.2 per 100,000, respectively). PCR-positive cases (compared to PCR-negative) had a two-fold increased risk of overall mortality. We observed a 24% higher risk of death in men than in women and in older patients than in younger ones. Patients residing in rural areas had a 66% higher risk of death compared to city residents, and being treated in a makeshift hospital was associated with 1.9 times higher mortality compared to those treated in hospitals of infectious diseases.
Conclusion
This is the first study from the Central Asia and Eurasia regions, assessing mortality from SARS-CoV-2 PCR positive and PCR negative respiratory system diseases during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic. We describe a higher mortality rate for PCR-positive cases compared to PCR-negative cases, for men compared to women, for older patients compared to younger patients, and for patients living in rural areas. rural compared to city residents.